An isolator is a one-way two-port, transporting incoming waves
lossless from the input (port 1) to the output (port 2), but dissipating
all waves flowing into the output.
The ideal isolator with reference impedances ![]() (input) and
(input) and ![]() (output) is determined by the following Z parameters (for DC and
AC simulation).
(output) is determined by the following Z parameters (for DC and
AC simulation).
| (9.88) |
| (9.89) |
A more useful MNA representation is with Y parameters.
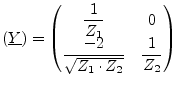 |
(9.90) |
Isolator with reference impedance ![]() (input) and
(input) and ![]() (output) and
temperature
(output) and
temperature ![]() :
:
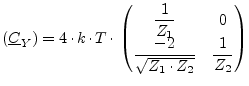 |
(9.91) |
With the reference impedance of the
input ![]() and the one of the output
and the one of the output ![]() , the scattering parameters
of an ideal isolator writes as follows.
, the scattering parameters
of an ideal isolator writes as follows.
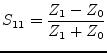 |
(9.92) |
| (9.93) |
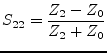 |
(9.94) |
| (9.95) |
Being on temperature ![]() , the noise wave correlation matrix of an
ideal isolator with reference impedance
, the noise wave correlation matrix of an
ideal isolator with reference impedance ![]() and
and ![]() (input and
output) writes as follows.
(input and
output) writes as follows.
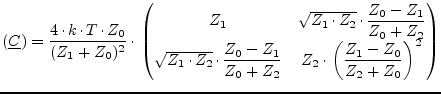 |
(9.96) |