![\includegraphics[width=4cm]{gyrator}](img1047.png)
|
A gyrator is an impedance inverter. Thus, for example, it converts a capacitance into an inductance and vice versa. The ideal gyrator, as shown in fig. 9.6, is determined by the following equations which introduce two more unknowns in the MNA matrix.
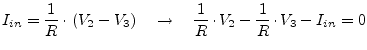 |
(9.133) |
The new unknown variables ![]() and
and ![]() must be considered by
the four remaining simple equations.
must be considered by
the four remaining simple equations.
| (9.135) |
As can be seen, a gyrator consists of two cross-connected VCCS (section 9.19.1). Hence, its y-parameter matrix is:
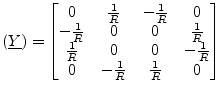 |
(9.136) |
The scattering matrix
of an ideal gyrator with the ratio ![]() writes as follows.
writes as follows.
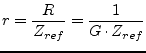 |
(9.137) |
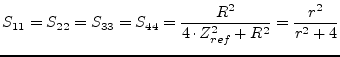 |
(9.138) |
| (9.139) |
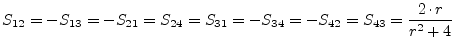 |
(9.140) |