![\includegraphics[width=0.6\linewidth]{spnfile}](img1178.png)
|
The Y-parameters of a multi-port component defined by its S-parameters required for a small signal AC analysis can be obtained by converting the S-parameters into Y-parameters.
In order to extend a ![]() -port to have a S-parameter device with
-port to have a S-parameter device with
![]() ports assuming that the original reference port had a reflection
coefficient
ports assuming that the original reference port had a reflection
coefficient ![]() the new S-parameters are according to
T. O. Grosch and L. A. Carpenter [12]:
the new S-parameters are according to
T. O. Grosch and L. A. Carpenter [12]:
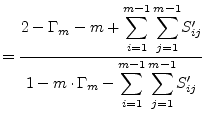 |
(9.227) | ||
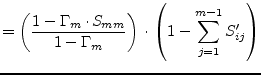 |
(9.228) | ||
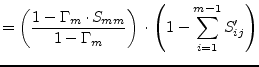 |
(9.229) | ||
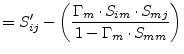 |
(9.230) |
If the reference port has been ground potential, then ![]() simply folds to -1. The reverse transformation by connecting a
termination with a reflection coefficient of
simply folds to -1. The reverse transformation by connecting a
termination with a reflection coefficient of ![]() to the
to the ![]() th
port writes as follows.
th
port writes as follows.
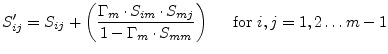 |
(9.231) |
With the S-parameter transformation done the ![]() -port noise wave
correlation matrix is
-port noise wave
correlation matrix is
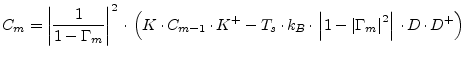 |
(9.232) |
with
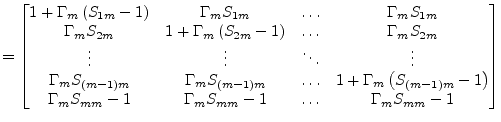 |
(9.233) | |
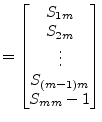 |
(9.234) |
whence ![]() denotes the equivalent noise temperature of the original
reference port and the
denotes the equivalent noise temperature of the original
reference port and the ![]() operator indicates the transposed
conjugate matrix (also called adjoint or adjugate).
operator indicates the transposed
conjugate matrix (also called adjoint or adjugate).
The reverse transformation can be written as
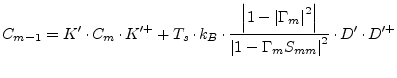 |
(9.235) |
with
 |
(9.236) | |
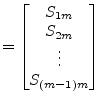 |
(9.237) |