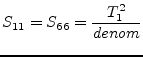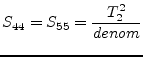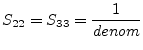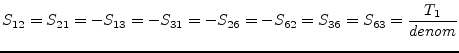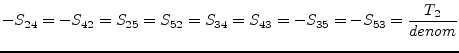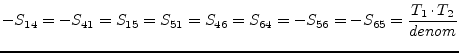The ideal symmetrical transformer, as shown in fig.
9.3, is determined by the following equations which
introduce two more unknowns in the MNA matrix.
Figure 9.3:
ideal three winding transformer
|
|
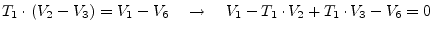 |
(9.30) |
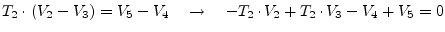 |
(9.31) |
The new unknown variables 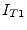 and
and 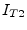 must be considered by
the six remaining simple equations.
must be considered by
the six remaining simple equations.
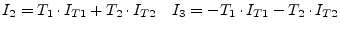 |
(9.32) |
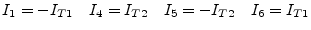 |
(9.33) |
The matrix representation needs to be augmented by two more new rows
and their corresponding columns. For DC and AC simulation it is:
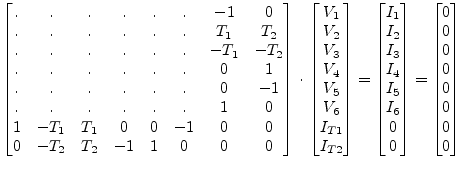 |
(9.34) |
Using the port numbers depicted in fig. 9.3, the
scattering parameters of an ideal, symmetrical transformer with
voltage transformation ratio (number of turns) 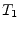 and
and 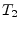 ,
respectively, writes as follows.
,
respectively, writes as follows.
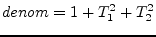 |
(9.35) |
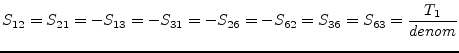 |
(9.39) |
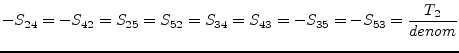 |
(9.40) |
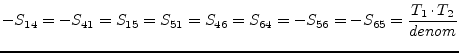 |
(9.41) |
An ideal symmetrical transformer is noise free.
This document was generated by Stefan Jahn on 2007-12-30 using latex2html.
![\includegraphics[width=4cm]{acstrafo}](img897.png)
![]() and
and ![]() must be considered by
the six remaining simple equations.
must be considered by
the six remaining simple equations.
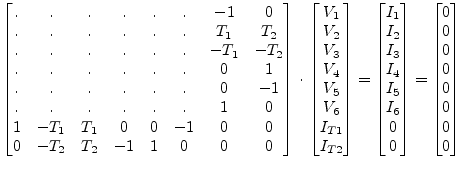
![]() and
and ![]() ,
respectively, writes as follows.
,
respectively, writes as follows.