| (2.4) |
Having the noise wave correlation matrix, one can easily compute the noise parameters [5]. The following equations calculate them with regard to port 1 (input) and port 2 (output). (If one uses an n-port and want to calculate the noise parameters regarding to other ports, one has to replace the index numbers of S- and c-parameters accordingly. I.e. replace "1" with the number of the input port and "2" with the number of the output port.)
Noise figure:
| (2.5) |
Optimal source reflection coefficient (normalized according to the input port impedance):
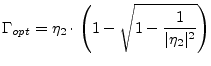 |
(2.6) |
| (2.7) |
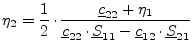 |
(2.8) |
Minimum noise figure:
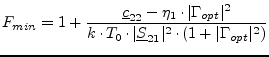 |
(2.9) |
| (2.10) |
Equivalent noise resistance:
| With |
|
| Boltzmann constant
|
|
| standard temperature |
Calculating the noise wave correlation coefficients from the noise parameters is straightforward as well.
| (2.12) |
| (2.13) |
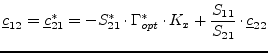 |
(2.14) |
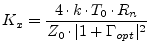 |
(2.15) |
Once having the noise parameters, one can calculate the noise figure for
every source admittance
![]() , source impedance
, source impedance
![]() , or source reflection coefficient
, or source reflection coefficient ![]() .
.
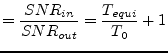 |
(2.16) | |
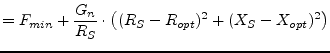 |
(2.17) | |
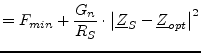 |
(2.18) | |
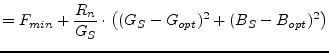 |
(2.19) | |
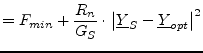 |
(2.20) | |
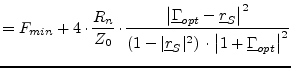 |
(2.21) |
Where ![]() and
and ![]() are the signal to noise ratios at the
input and output, respectively,
are the signal to noise ratios at the
input and output, respectively, ![]() is the equivalent (input)
noise temperature. Note that
is the equivalent (input)
noise temperature. Note that ![]() does not equal
does not equal ![]() .
.
All curves with constant noise figures are circles (in all planes, i.e. impedance, admittance and reflection coefficient). A circle in the reflection coefficient plane has the following parameters.
center point:
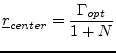 |
(2.22) |
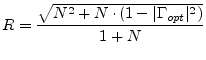 |
(2.23) |
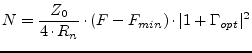 |
(2.24) |